Tobacco Addiction Treatment
Tobacco addiction is a pervasive issue that affects millions of people globally. Despite extensive knowledge of its harmful effects and the widespread anti-smoking campaigns, quitting tobacco remains a significant challenge for many individuals. Tobacco use, whether through smoking cigarettes or using smokeless tobacco products, poses severe health risks and impacts overall well-being. If you or someone you know is struggling with tobacco addiction, understanding the nature of the addiction and exploring effective treatment options is crucial for achieving recovery and improving quality of life.
Understanding Tobacco Addiction
Tobacco addiction primarily involves dependence on nicotine, a highly addictive substance found in tobacco products. Nicotine addiction develops as the brain becomes accustomed to the stimulating effects of nicotine, leading to cravings and withdrawal symptoms when the substance is not present. Tobacco addiction often becomes a deeply ingrained habit, associated with various daily routines and stressors, making it difficult to quit.
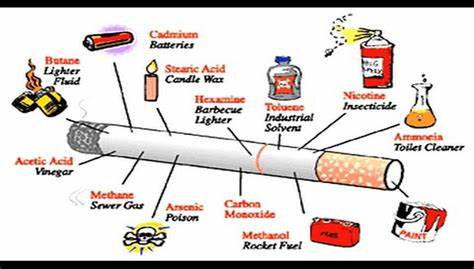
The Impact of Tobacco Addiction
Tobacco addiction has far-reaching effects on various aspects of an individual’s life:
Physical Health
Tobacco use is a major cause of serious health issues, including lung cancer, COPD, heart disease, stroke, and various cancers. It also leads to respiratory infections, reduced lung function, and overall health decline.
Mental Health
The cycle of addiction and withdrawal can lead to mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and mood swings. The stress of trying to quit and dealing with cravings can further exacerbate these conditions.
Financial Costs
well-being.
Social and Professional Life
self-image.
Impact on Loved Ones
The Role of Family and Friends
Support from family and friends is a vital component of successful tobacco cessation. Loved ones can provide encouragement, offer practical assistance, and help manage challenges during the quitting process. Family and friends can also benefit from learning about tobacco addiction and supporting the individual in a non-judgmental and understanding manner.
Overcoming Stigma and Barriers to Treatment
Tobacco addiction is often stigmatized, and individuals may feel embarrassed or ashamed about seeking help. It’s important to recognize that addiction is a medical condition that requires treatment. Overcoming stigma involves promoting awareness, understanding, and compassion for those struggling with tobacco addiction.
Finding the Right Treatment Program
Choosing the right treatment program is crucial for successful tobacco cessation. Look for a facility that offers a comprehensive approach, including medical support, behavioral therapy, and ongoing support. A personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs and circumstances is essential for achieving lasting results.
Why Treatment is Essential
Quitting tobacco is challenging due to the physical addiction to nicotine and the psychological habits associated with tobacco use. Many individuals attempt to quit on their own but find it difficult due to withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Professional treatment provides structured support, medical assistance, and behavioral therapies that significantly increase the chances of successfully quitting tobacco.
Treatment Approaches for Tobacco Addiction
Effective treatment for tobacco addiction involves a combination of medical, therapeutic, and behavioral interventions. Here are some of the most common and effective approaches:
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT)
NRT helps to alleviate withdrawal symptoms by providing a controlled dose of nicotine without the harmful chemicals found in tobacco products. Common forms of NRT include:
- Nicotine Patches: Worn on the skin and provide a steady release of nicotine throughout the day.
- Nicotine Gum: Allows for intermittent dosing of nicotine to help manage cravings.
- Nicotine Lozenges: Dissolve in the mouth to release nicotine and help reduce cravings.
- Nicotine Nasal Spray: Delivers nicotine through the nasal membranes.
- Nicotine Inhalers: Provide a vaporized form of nicotine that is inhaled.
Prescription Medications
Several prescription medications can assist with quitting tobacco by reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms. These include:
- Bupropion (Zyban): A prescription medication that helps reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain.
- Varenicline (Chantix): Works by reducing withdrawal symptoms and cravings while also decreasing the pleasure associated with tobacco use.
Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy helps individuals address the psychological and emotional aspects of tobacco addiction.
Support Groups
Support groups offer a sense of community and shared experience for individuals trying to quit tobacco. Participating in a support group can provide encouragement, reduce feelings of isolation, and offer practical tips and strategies from others who have successfully quit.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting healthy lifestyle changes can support tobacco cessation and improve overall well-being. These changes may include:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can reduce stress, improve mood, and help manage weight gain often associated with quitting tobacco.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet can support physical health and reduce cravings.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises can help manage stress and prevent tobacco use as a coping mechanism.
Relapse Prevention
Relapse prevention strategies are crucial for maintaining long-term success. These strategies may include:
- Developing Coping Skills: Learning effective ways to handle stress, triggers, and cravings.
- Building a Support Network: Engaging with family, friends, and support groups to stay motivated and accountable.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Establishing achievable milestones and celebrating progress along the way.
Conclusion
Tobacco addiction is a serious and complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to treatment. Understanding the nature of addiction, exploring effective treatment options, and seeking professional help are essential steps in achieving recovery. With commitment and support, it is possible to quit tobacco and lead a healthier, more fulfilling life.